Canada stares down consequences of Trump tariff war: Job losses, grocery price hikes, possible recession
Canada is bracing for the fallout of President Donald Trump’s escalating trade war, with economists warning of spiking grocery prices, major job losses and even a potential recession if threatened U.S. tariffs take effect.
The United States is Canada’s largest trading partner, accounting for nearly two-thirds of Canadian imports and receiving over 70% of its exports. But under Trump’s new “liberation day” tariffs – 25% on Canadian goods and 10% on energy – Ottawa now faces an economic gut punch that could ripple across key provinces, industries and its national election campaign.
Trump has repeatedly blasted what he calls “unfair” trade practices, citing Canada’s trade imbalance with the U.S. to justify the sweeping tariffs.
“This is the beginning of liberation day in America,” Trump said last week. “We’re going to charge countries for doing business in our country and taking our jobs, taking our wealth, taking a lot of things that they’ve been taking over the years. They’ve taken so much out of our country, friend and foe. And, frankly, friend has been oftentimes much worse than foe.”
TRUMP’S 11TH WEEK IN OFFICE SET TO FOCUS ON TARIFFS AS PRESIDENT TOUTS ‘LIBERATION DAY’
Canadians protest U.S. tariffs and other policies of President Donald Trump in Toronto on March 22, 2025. (REUTERS/Carlos Osorio)
Increased tariffs could mean that Americans will see higher price tags on everything ranging from fertilizer and oil, vehicles and machinery, to plastic and wood products, which, theoretically, would deter consumers from purchasing those products and result in a loss for Canada’s economy.
Likewise, Canada in mid-March implemented reciprocal tariffs on $30 billion worth of U.S. goods, which means Canadians will not only feel losses on a macro scale but also in an immediate sense as prices at the grocery store have spiked on things like leafy greens, citrus, orange juice, beef, pork and fish.
Ottawa has yet to announce any tariffs on U.S. imported vehicles due to reported concerns over how it could further hinder Canada’s economy. Though there are some $95 billion worth of U.S. goods that it is reportedly considering putting tariffs on, depending on Trump’s April 2 announcements, according to Canadian outlet Financial Post.
“They’re in the midst of a general election campaign,” Andrew Hale, a senior policy analyst in trade policy with the Heritage Foundation, told Fox News Digital. “I think it’s very difficult for them to negotiate and put these measures on during an election campaign.
“Everything they do and say now carries electoral weight,” he added, noting that Canadian politicians will need to strike a careful balance: tough enough on Trump to appeal to voters but measured enough to leave room for future negotiations on tariffs.
“If they were to put on reciprocal tariffs, it would damage the Canadian standard of living and have an impact – as all this already is having an impact – in Canada,” Hale said, noting that auto tariffs not only affect direct car sales but all businesses that rely on vehicles, creating a trickle-down effect.
CANADIANS CLAIM THEY ARE CANCELING TRIPS TO US FOR REMAINDER OF TRUMP TERM

Canadian Liberal Party leader Mark Carney speaks to supporters during a rally in Montreal on March 27, 2025. A federal election has been called, and Canadian voters go to the polls on April 28. (Andrej Ivanov/Getty Images)
While Trump has argued that his tariffs protect U.S. manufacturing – especially the auto sector – the fallout could be far more severe for Canada. Immigration Minister Marc Miller has warned that up to 1 million Canadian jobs are at risk.
“Most Canadians live within 100 miles of the U.S.-Canadian border, and so they obviously will be heavily impacted,” said Hale. “Most Americans don’t.”
Hale noted that while the tariffs will affect the entire U.S., the hardest-hit areas will be industries closely tied to Canadian imports, such as agriculture. The U.S., for instance, sources 90% of its potash fertilizer from Canada.
“This will have a disproportionate impact on border states,” Hale said, but he added that the economic strain on Canadian regions like Ontario will be far greater.
Canadian leaders have already voiced concern that as many as 160,000 jobs could be lost in Quebec, along with another 500,000 jobs in Ontario, depending on how long the tariff dispute lasts.
Both Quebec and Ontario are two of the provinces expected to be among those hardest hit in Canada as they rely heavily on their steel and aluminum and lumber and forestry sectors for exports.
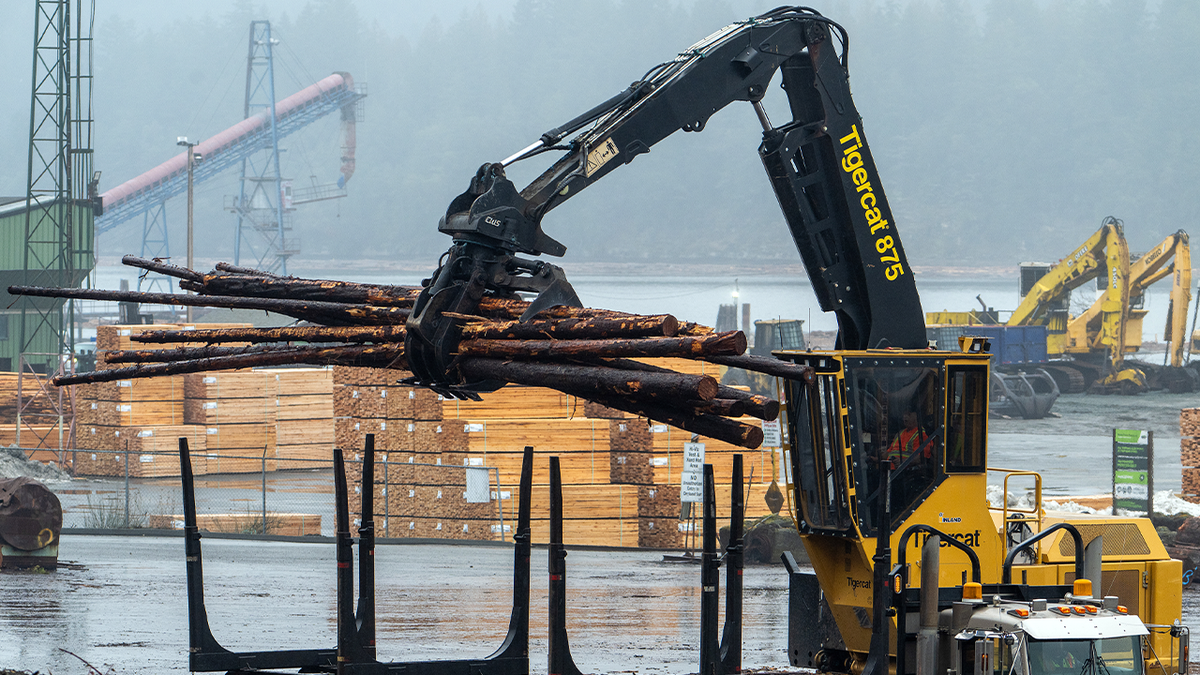

A worker loads logs onto a truck at the Western Forest Products Ladysmith Log Sort in Ladysmith, British Columbia, Canada, on Feb. 18, 2025. Canada is the U.S.’ biggest foreign lumber supplier and has already been dealing with higher duties on its shipments that started last summer. (James MacDonald/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
Canada could face a recession this year if it can’t rein in Trump’s tariff offensive, Oxford Economists first warned in a report last November.
Previous tariff wars between trading partners during the first Trump administration resulted in billions of dollars of losses for Americans and their foreign counterparts.
TRUMP HOLDS ‘EXTREMELY PRODUCTIVE CALL’ WITH CANADIAN PRIME MINISTER: ‘WE AGREE ON MANY THINGS’
But Trump is banking on the U.S. being less severely affected than nations like Canada.
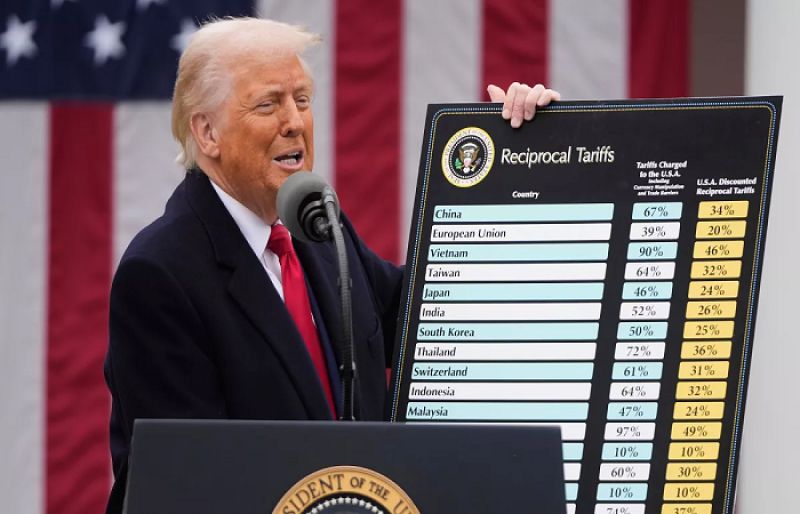
The full impact of the tariff war with Canada remains uncertain as Washington has also imposed steep tariffs on the European Union, China and Mexico. Trump has pledged to target the “Dirty 15,” which are countries he accuses of contributing most to the U.S. trade deficit.
Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, South Africa, South Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam are expected to be among those next targeted in Trump’s April 2 tariff announcement, which he has dubbed “liberation day.”
Details on what Trump’s next steps in his tariff war with Canada and dozens of other nations remain unknown ahead of the April 2 deadline, which has created a sense of uncertainty, Hale said.
“Last week’s Bureau of Economic Analysis Reports signaled a continued high core personal consumption expenditure PC inflation at 2.8%. So inflation, one could argue, is not coming down, and certainly price levels continue to rise,” he said. “Consumer spending has slowed sharply in both Canada and the United States.”

President Donald Trump delivers remarks after signing an executive order on reciprocal tariffs in the Oval Office on Feb. 13, 2025. (Andrew Harnik/Getty Images)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
“Businesses want certainty. They can’t make future investment decisions in this climate,” he added, noting that while a recession could be on the horizon in Canada, there are too many variables to make a prediction on the U.S. at this time.
“What I do know is that businesses and banks, people who are investing in projects, want to be able to plan,” Hale said. “Hopefully, we’ll have a clear idea [on Tuesday] where this is all going to land, and then we can work with it.”