Heart Attack vs Cardiac Arrest: Knowing The Difference Could Be A Lifesaver – News18
Last Updated:
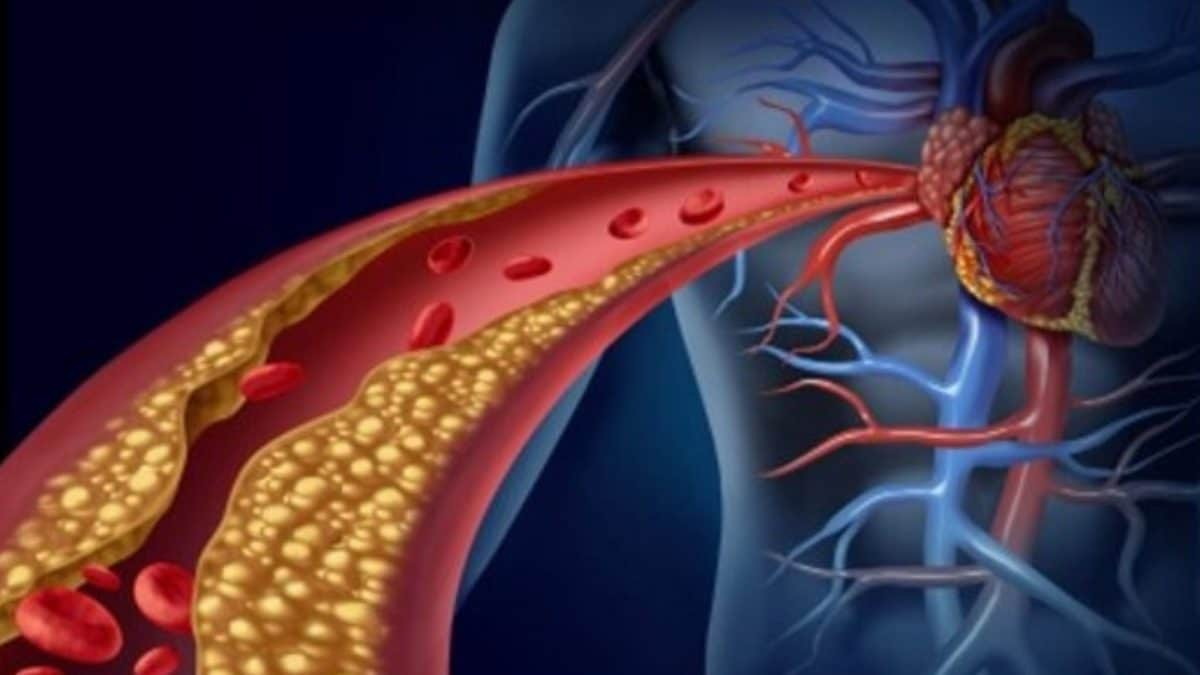
A heart attack occurs when blood flow is interrupted due to a blockage in the heart’s arteries. On the other hand, in cardiac arrest, the heartbeat stops abruptly, which can cause the patient to faint or die suddenly
Unusual discomfort, heaviness, burning, tightness, or pain in the chest lasting no more than 30 minutes or recurring could indicate a heart attack. (News18 Hindi)
Due to changing lifestyles and increasing stress, heart-related diseases are rapidly rising. But did you know that heart attack, cardiac arrest, and heart blockage are three distinct medical conditions?
Speaking to Local18, professor and heart specialist at Satna Medical College, Dr LP Singh, stated that if these conditions are identified promptly and treated immediately, the patient’s life can be saved.
Difference Between A Heart Attack And Cardiac Arrest
The expert explained that a heart attack occurs when blood flow is interrupted due to a blockage in the heart’s arteries. On the other hand, in cardiac arrest, the heartbeat stops abruptly, which can cause the patient to faint or die suddenly. If CPR is administered on time, the chances of saving the patient’s life increase significantly.
Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Unusual discomfort, heaviness, burning, tightness, or pain in the chest lasting no more than 30 minutes or recurring could indicate a heart attack. Many patients dismiss it as gas, but it can be a serious warning sign.
Symptoms such as pain in the jaw, neck, back, shoulder, or both arms, difficulty breathing, dizziness, vomiting, cold sweats, and unexplained fatigue should not be ignored. In such situations, getting an ECG immediately is crucial.
100% Blockage Means Direct Heart Attack
When the blockage in the main arteries of the heart reaches 100%, it becomes a medical emergency. In such cases, if a person suffers a heart attack, first check their pulse and immediately administer CPR. Pump the chest vigorously with both hands until medical help arrives. This helps maintain blood circulation and can prevent brain and kidney damage. In many cases, prompt CPR can restart the heartbeat and save the patient’s life.
Do’s and Don’ts
- If there is even the slightest doubt, get an ECG done immediately.
- Do not rely on balm or home remedies in case of a heart attack.
- Administering CPR within 10-20 seconds can save the patient’s life.
- A lipid profile or cholesterol test is not immediately necessary; prioritise getting an ECG first.










