The Role of Fascia in Musculoskeletal Health: New Techniques for Fascia Care – News18
Last Updated:
By understanding and addressing fascia’s role in the body, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their musculoskeletal well-being, ensuring long-term flexibility and comfort.
Poor posture, repetitive motions, and lack of flexibility can lead to tightness and irritation in the fascia, resulting in pain and restricted mobility
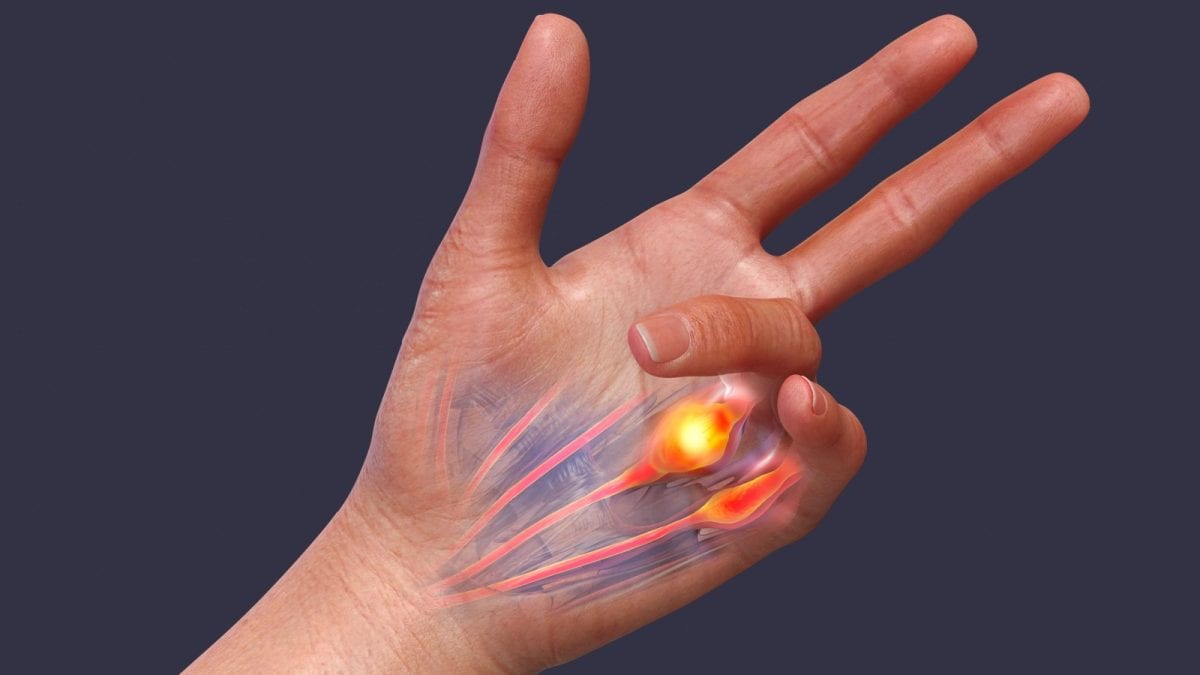
Often overlooked, fascia plays a critical role in maintaining musculoskeletal health, mobility, and overall well-being. This intricate network of connective tissue wraps around muscles, bones, and internal organs, providing structural support while facilitating movement. However, poor posture, repetitive motions, and lack of flexibility can lead to tightness and irritation in the fascia, resulting in pain and restricted mobility. Experts highlight the importance of fascia health and explore the latest techniques to keep it supple and functional.
Fascia Therapy: Techniques to Enhance Flexibility and Well-being
According to Dr. Brahmaraju T J, Senior Consultant – Orthopaedics & Joint Replacement Surgery, Gleneagles BGS Hospital, Kengeri, Bengaluru, fascia therapy influences not only physical health but also emotional well-being. “Stretching or massaging the fascia has a holistic impact, regulating muscle tone, digestion, immunity, respiration, and even mental health,” he explains. Various techniques help in maintaining fascia flexibility and function:
Foam Rollers: These help loosen and soften fascia, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Myofascial Release: Performed by trained professionals, this technique targets specific sites to release tension.
Trigger Point Therapy: This involves applying pressure to precise points to alleviate tightness in the fascia.
Acupuncture: The use of fine needles helps release fascial tension and improve flexibility.
Physical Therapy: Techniques such as ultrasonic massage, heat, and cold therapy contribute to fascia relaxation and improved mobility.
The Connection Between Fascia and the Nervous System
Fascia is not just a structural component—it is deeply intertwined with the nervous system. “Fascia contains over 250 million nerve endings, making it the largest sensory organ in the body,” states Dr. Brahmaraju. He emphasizes that impaired fascia can affect proprioception (the body’s ability to sense movement and position) and increase pain perception. “For instance, chronic low back pain is often linked to thickened or hardened fascia in the back. Ensuring fascia remains healthy is crucial for a well-functioning nervous system and pain management.”
Preventing and Addressing Fascia Problems
Dr. Sanjib Kumar Behera, Clinical Director & HOD, Dept. of Orthopaedic and Joint Replacement Surgery, CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, underscores the importance of proactive fascia care. “This dense webbing supports movement and anchors muscles and bones, but it can become problematic due to bad posture, repetitive motions, or prolonged inactivity,” he notes. Tight or irritated fascia can lead to conditions such as heel pain, restricted flexibility, and chronic soreness.
To prevent such issues, Dr. Behera suggests maintaining fascia pliability through:
Hydration: Keeping the body well-hydrated supports fascia elasticity.
Regular Movement: Avoiding prolonged inactivity and incorporating stretches into daily routines can prevent stiffness.
Good Posture: Proper alignment reduces unnecessary stress on the fascia.
Early Intervention: Addressing fascia-related discomfort early can improve long-term musculoskeletal health and overall quality of life.
The Future of Fascia Health
New therapies, including regenerative treatments and myofascial release techniques, continue to advance fascia care. Whether through self-care methods like foam rolling or professional interventions, prioritizing fascia health can lead to better mobility, reduced pain, and improved physical resilience.
By understanding and addressing fascia’s role in the body, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their musculoskeletal well-being, ensuring long-term flexibility and comfort.