This Fungicide Could Save Your Roses This Spring— How to Use It Like a Pro
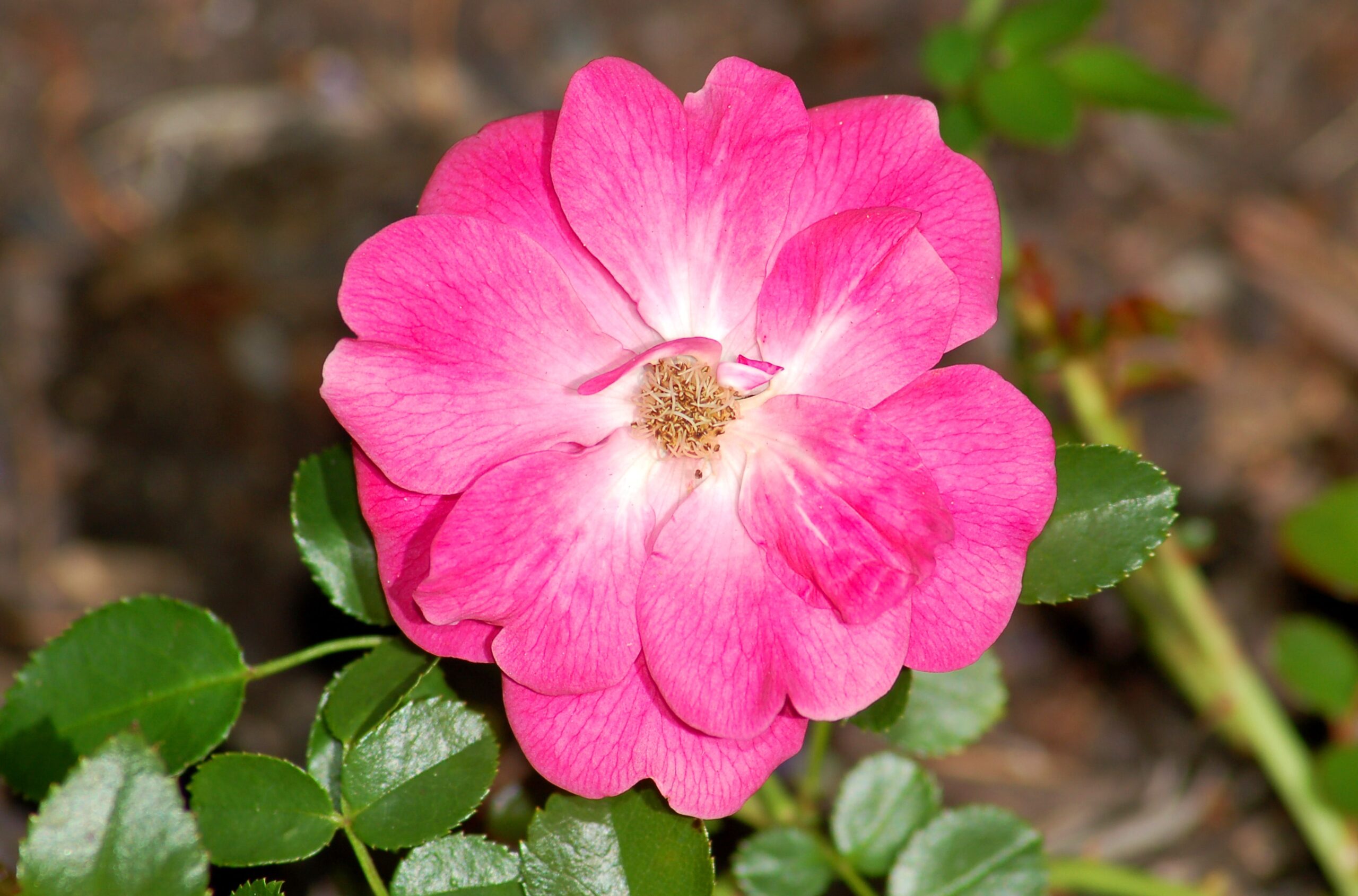
If you have trouble with fungal or bacterial diseases in your garden, Bordeaux mixture may be able to help. For example, if you grow roses, you may have problems with diseases such as anthracnose, rust, leaf spot, or powdery mildew.
Growers of both apple trees and crabapple trees commonly face apple scab. Peachtree growers have to fight leaf curl, while fire blight is an issue for pear trees. Applying the Bordeaux mixture can help you prevent those diseases.
Learn what Bordeaux mixture is, what you need to make it, how and when to apply, and what plants profit from the application.
What Is Bordeaux Mixture?
Bordeaux mixture is a fungicide used in fall and winter (when the plants are dormant) to control any fungus or bacteria that will attack certain plants in spring. It is composed of copper sulfate, hydrated lime, and water.
Copper sulfate and hydrated lime are powdery substances sold by the bag at some garden centers (you can also buy some that have already been mixed for you). When mixing, use a container that will hold more than 1 gallon. Add the ingredients to that container in the following proportions:
- 1 gallon of water
- 1/10th pound of copper sulfate (3 1/3 tablespoons)
- 1/10th pound of hydrated lime (10 tablespoons)
Make sure the ingredients are thoroughly mixed.
Want more gardening tips? Sign up for our free gardening newsletter for our best growing tips, troubleshooting hacks, and more!
Plants That Need Bordeaux Mix
Many commonly grown plants can profit from an application of the Bordeaux mixture. Plants in the Rosaceae family are particularly susceptible to fungal disease invasions. This includes the following edible and ornamental plants:
- Roses (Rosa genus)
- Apple trees (Malus genus)
- Pear trees (Pyrus communis)
- Crabapple trees (Malus genus)
- Plum trees (Prunus genus)
- Peach trees (Prunus persica)
- Bing cherry trees (Prunus avium ‘Bing’)
- Cotoneaster shrubs (Cotoneaster genus)
How to Use Bordeaux Mixture
As useful as Bordeaux mixture may be, it is important to apply it properly. Follow these five application tips for protecting your plants:
- Apply Bordeaux mixture during the dormant season: Bordeaux mixture is applied when plants do not have their leaves. If you apply it in spring or summer, it may damage the plants’ foliage.
- Use a power sprayer to apply (preferred method): Application is easier if you have a power sprayer.
- You can also use a hand sprayer (alternative method): If you do not own a power sprayer, you can still spray Bordeaux mixture. Fill a hand sprayer with the mix from your mixing container and keep refilling until the job’s done.
- Thorough coverage is important: When spraying, be sure to cover as much of the plant as possible.
- Apply annually: This is not a one-and-done project. You will have to re-apply the Bordeaux mixture every fall or winter after the leaves have dropped from the targeted deciduous plants.